The Rise of the GCCs: Changing Narratives & Globalisation 2.0
February 18, 2025
|
The Rise of the GCCs: Changing Narratives & Globalisation 2.0
February 18, 2025
|The perception of India on the global stage has changed for the good ever since PM Modi took over in 2014. India needed that - for the growth and advancement of its 1.45bn people. Prior to his ascendance as PM, India was viewed as a third-world country rather than the single-largest, fastest-growing, modernizing emerging economy that it truly is.
Global Capability Centre (GCC). - Sounds sophisticated and “corporate”, right?
That’s because it is!
But what do GCCs have to do with the above-mentioned narrative change? & why are they seemingly so important?
In this article, we discuss how GCCs have a lot to do with the changing perception of India on the global stage, and how it’s going to play a significant role in propelling India into its next phase of growth and development.
Introducing GCCs
Earlier, India was seen purely as an outsourcing destination for business services or large conglomerates (mainly multinationals), that could outsource their non-essential, labour-intensive operations to it. This meant that Indians would get access to only the less intellectual and mundane jobs that required the most basic skills and education. However, this has drastically changed over the last decade or so.
Global Capability Centres, or GCCs are company subsidiaries set up in a country other than that of the parent company that carry out one or more critical business functions for the parent.

Overview of the GCC Ecosystem in India
Today, India’s GCC ecosystem majorly resides in the metros, namely Bengaluru, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Mumbai and Chennai. The following chart shows the breakdown of the number of GCCs in India, according to a recent report by Teamlease Digital:
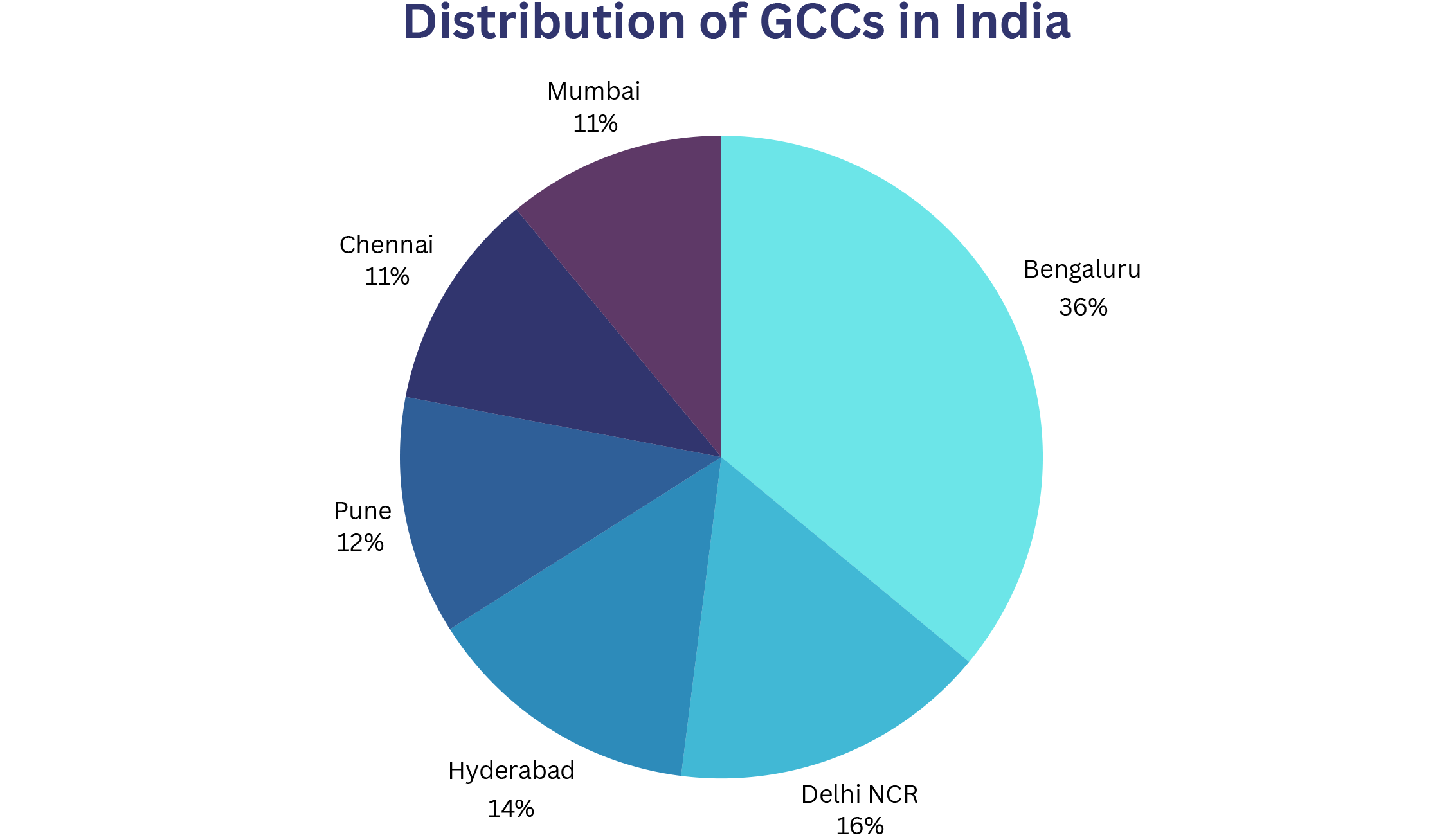
Bengaluru alone accounts for nearly 36% of the total GCCs in India!
Fun Fact: The Government of Karnataka has its own GCC Policy that aims to create 3.5 lakh jobs by the year 2029, via the addition of over 500 GCCs, while taking the total GCCs in the state to 1,000.
Which companies are setting up GCCs?
- GCCs are usually set up by large conglomerates like Microsoft, Siemens, Accenture, Deutsche Bank, Morgan Stanley, Ericsson, Abbott, and Cummins, which have global operations spanning several countries.
- In the APAC region, companies like Samsung, Hyundai, Panasonic, and Hitachi have already set up GCCs in India. Conglomerates like Reliance Industries, Adani Group, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, and Bank of Baroda are other notable names in the GCC ecosystem.
- As of 2023, at least 20% of Fortune 200 global companies have established GCCs in India, a figure that is projected to increase by 50% by 2030.
To get a sense of scale of this ecosystem, please see the chart below:

With over 50% share in the Global GCC destinations, India ranks as the top choice for conglomerates globally, especially Europe and the US.
The Scale of GCCs is becoming hard to ignore.
The post-Covid boom had many gifts to give, one of which was the rising prominence of the GCC ecosystem in India. It's not that they were not present in India before Covid, but the fact that they are now rising to prominence is something we’re trying to highlight here.
There are over 1700 companies that have set up GCCs in India, and the number is ever-increasing. To get a sense of the trend, take this: In 2010, the number of GCCs in India was 700; in 2016 this number was 1,000, and in 2023 this number touched 1,600.
With their current annual revenue run rate, GCCs account for >1% of India's GDP, making it a major driver of economic growth. This number is expected to go up to 3.5% by 2030, according to economic surveys.
Over the past 4-5 years, the GCC offices of global MNCs have evolved from single-function in-house centers to multifunction or hybrid models, enhancing their capabilities to play a greater role in the MNC's global operations.
What’s driving this rise to prominence?
Some of the reasons why GCCs have risen to prominence are:
- Copious supply of low-cost, Intellectual talent:
- Access to Cheaper Land: which may be subsidised by the government.
- Government Support in setting up GCCs: Streamlined Tax regulations and compliance procedures, along with flexible labor laws.
- Digital India & India Stack: Serves as a backbone for the interactions between the public, private, and the government. Eg. Online Approvals and Licensing, single window clearances, etc.
- Manufacturing incentives, liberal FDI norms.
- Stable political environment that encourages entrepreneurship, risk taking and innovation
- Availability of Digital Infrastructure: High speed, low-cost internet, and a burgeoning data center capacity that is scaling.
GCCs are the bedrock of Innovation and R&D
GCCs are increasingly being seen as the epicentre for new initiatives in Research and Development within the country. Any R&D initiative requires a mix of talent, financial and infrastructure resources, along with solid institutional backing - GCCs are exactly that. Flush with financial resources from their global parent companies, GCCs have the firepower to encourage research initiatives, that may take a while before any meaningful results show. But, as history has shown in the case of China, over 2 decades of R&D efforts paid off over the next 20 years! And they paid off handsomely, making China a world leader in several disciplines and numerous industries.
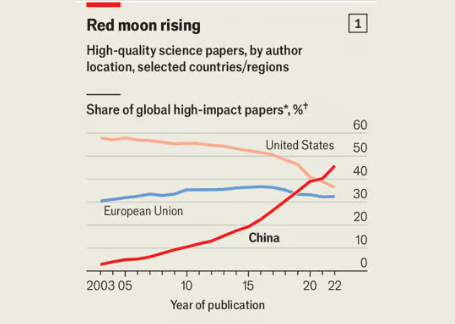
Source: The Economist
China’s story is a golden example of how relentless focus on research can drive economic development in a country. Nithin Kamath wrote about this in his recent blog post, and I quote, “I saw this chart in an Economist article. It gives you a quick and dirty idea of the progress China has made despite the fact that papers and citations can be gamed. India wouldn’t even show up on the chart.”
At the Forefront of the Technological Curve
GCCs are building an ecosystem that is at the leading end of the technological curve. This is evident by the range of domains that the GCCs specialize in. Areas like Software, ER&D, Semiconductors, Data Analytics, Digital Transformation and Cloud Services, robotic process automation (RPA), DevOps, Cybersecurity and AI/ML engineering are seeing increased traction in the GCC ecosystem.
On the engineering & manufacturing side, sectors with high levels of technical expertise are gaining traction, for eg. Electricals & Electronics, Heavy Machinery, Automotive, and Semiconductors, among others.
Going forward, such Centres of Excellence are expected to drive product/service innovations and handle a greater share of complex technology-driven work for the parent organizations who will be looking to accelerate business recovery while focusing on the next level of growth.
The economic Impact of GCCs
The largest contributing state, Karnataka alone has set an ambitious goal of setting up 500 GCCs by 2029, creating an economic output of $50bn in the process.
India itself is expected to reach a revenue potential of over $100-110bn by 2030, on the back of sustained influx of GCCs into the country, and the revenue growth from the existing centres.
The Migration of Talent from IT hubs to GCCs
Another noticeable change observed was that of IT capability centres shifting from IT Parks/Hubs to dedicated GCC offices.
GCCs are offering ample space, value, and opportunities for long-term projects to teams from IT companies. At the same time, it also makes sense for IT companies to outsource teams from their resource pool to complete the GCC clients ‘s projects on-campus.
On top of it, IT professionals may prefer such projects as it gives them the avenue to pursue high-quality intellectual projects with learning opportunities, along with strong prospects of career advancement and remuneration.
In addition, GCCs also tend to be more efficiently connected and backed by robust infrastructure, which works in their favour.
Nevertheless, the current model remains that both IT Parks and GCCs working hand in hand. However, GCCs may lead the front on R&D & innovation-specific projects that require the best talent and resources.
Closing Note
GCCs - More Than an Overseas Office
Industry experts believe that GCCs are increasing beginning to function as efficiently as any other revenue generating centre operating under their parent MNC corporations. This is proof of the rising prominence of the same in the context of economic development in India.
GCCs are the living example of “globalization in practice” and its positive impact on any country in general.
















 Continue with Google
Continue with Google