Mastering Moving Averages: A Comprehensive Guide for Stock Selection and Trading
March 11, 2024
|
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of stock trading, where volatility reigns supreme and decisions are made in split seconds, having the right tools at your disposal can make all the difference. Charts provide a factual representation of the price performance of numerous stocks. The price changes are a direct outcome of the daily supply and demand dynamics. Investors who dedicate themselves to understanding and interpreting price movements on charts gain a significant advantage over those who either refuse to learn, lack knowledge, or exhibit laziness. Just as you wouldn't fly in a plane without instruments or embark on a long cross-country trip without a road map, charts serve as your investment road map. Among various technical tools, moving averages stand out as one of the most versatile and widely used indicators. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of moving averages, exploring their calculation methods, interpretation techniques, practical applications, and more. Whether you're a novice investor looking to grasp the basics or a seasoned investor seeking advanced strategies, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to leverage moving averages effectively in your stock selection and trading endeavors.
Understanding Moving Averages
What are Moving Averages?
Moving averages, often abbreviated as MAs, are statistical indicators used to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specified period. Unlike raw price charts, which can be erratic and prone to fluctuations, moving averages provide a clearer picture of the underlying trend by filtering out noise and highlighting long-term patterns.
The Significance of Moving Averages
Moving averages serve multiple purposes in stock trading:
Trend Identification: By plotting moving averages on a price chart, investors can easily visualize the direction of the trend, whether it's bullish (upward), bearish (downward), or sideways (lateral).
Support and Resistance Levels: Moving averages act as dynamic support and resistance levels, helping invesstors identify potential entry and exit points. When prices approach a moving average from below, it often serves as a support level, while prices nearing from above may encounter resistance.
Price Reversal Signals: Moving average crossovers, where shorter-term averages intersect with longer-term ones, are commonly used as signals for trend reversals. These crossovers, such as the golden cross and death cross, can provide valuable insights into market sentiment shifts.
Types of Moving Averages
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The simple moving average is the most basic form of moving average, calculated by summing up the closing prices of a security over a specified period and dividing by the number of periods. SMAs provide a smooth representation of price trends and are widely used in various trading strategies.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
The exponential moving average is a more advanced variation of the simple moving average, giving greater weight to recent price data. This weighting scheme allows EMAs to respond more quickly to price changes, making them popular among short-term investors and trend followers.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
The weighted moving average assigns different weights to each price data point, with more recent prices receiving higher weights. While similar to EMAs in terms of responsiveness, WMAs offer greater flexibility in adjusting the weighting scheme to suit specific trading preferences.
Calculating Moving Averages
Simple Moving Average Calculation
The formula for calculating a simple moving average is straightforward:
SMA=
C1+C2+C3+...+Cn
n
Where:
- C1,C2,C3,...,Cn = Closing prices for each period
- n = Number of periods
Each new data point replaces the oldest one in the calculation, resulting in a continuous updating of the moving average.
Exponential Moving Average Calculation
The exponential moving average calculation involves a more complex formula:
EMA=(Close−EMAprevious)×α+EMAprevious
Where:
- Close = Current closing price
- EMAprevious = Previous EMA value
- α = Smoothing factor (typically derived from the number of periods)
The smoothing factor determines the rate at which the EMA reacts to new price data, with higher values resulting in faster adjustments.
Interpreting Moving Averages
Trend Analysis
Moving averages play a crucial role in trend analysis, helping investors identify the prevailing market direction. A rising moving average indicates an uptrend, while a falling moving average suggests a downtrend. By observing the slope and positioning of moving averages, investors can make informed decisions about trade entries and exits.
Support and Resistance Identification
Moving averages act as dynamic support and resistance levels, guiding investors in setting stop-loss orders and profit targets. When prices bounce off a moving average repeatedly, it reinforces its significance as a support or resistance level. Investors often use these levels to gauge the strength of a trend and anticipate potential price reversals.
Moving Average Crossovers
One of the most popular trading signals generated by moving averages is the crossover, where two moving averages intersect. The golden cross, occurring when a shorter-term average crosses above a longer-term one, signifies a bullish trend reversal. Conversely, the death cross, marked by a shorter-term average crossing below a longer-term one, indicates a bearish trend reversal.
Practical Applications of Moving Averages
Trend Following Strategies
Moving averages form the backbone of trend-following strategies, where investors aim to capitalize on sustained price movements in the direction of the trend. By aligning their trades with the prevailing market direction indicated by moving averages, trend followers seek to ride out profitable trends while minimizing losses during corrective phases.
Mean Reversion Strategies
In contrast to trend-following strategies, mean reversion strategies rely on the premise that prices tend to revert to their mean or average levels over time. Investors employing this approach use moving averages as reference points to identify overbought and oversold conditions, entering trades when prices deviate significantly from their average values.
Volatility-Based Strategies
Moving averages can also be used in volatility-based strategies, where investors adjust their trading parameters based on market volatility levels. By incorporating volatility measures such as average true range (ATR) into moving average calculations, investors can adapt their trading strategies to changing market conditions and optimize risk management.
Advanced Techniques and Tools
Multiple Moving Average Systems
Some investors combine multiple moving averages of varying lengths to form trading systems with enhanced signal quality and reliability. By incorporating short-term, medium-term, and long-term moving averages into their analysis, investors can filter out noise and identify high-probability trading opportunities with greater precision.
Moving Average Envelopes
Moving average envelopes are bands plotted above and below a moving average, representing predefined percentage deviations from the average. These envelopes act as dynamic support and resistance zones, providing investors with additional reference points for setting stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The moving average convergence divergence (MACD) is a popular momentum oscillator that combines two moving averages—a fast line (typically EMA) and a slow line (typically SMA). By comparing the convergence and divergence of these moving averages, investors can identify potential trend reversals and momentum shifts with greater accuracy.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Moving Averages in Action: Case Study 1
Let's examine a real-life example of how moving averages can be applied in stock trading. Suppose we have a chart showing the price movements of a particular stock over the past year. By overlaying various moving averages on the chart and analyzing their interactions with price action, we can identify key trading signals and opportunities for profit.
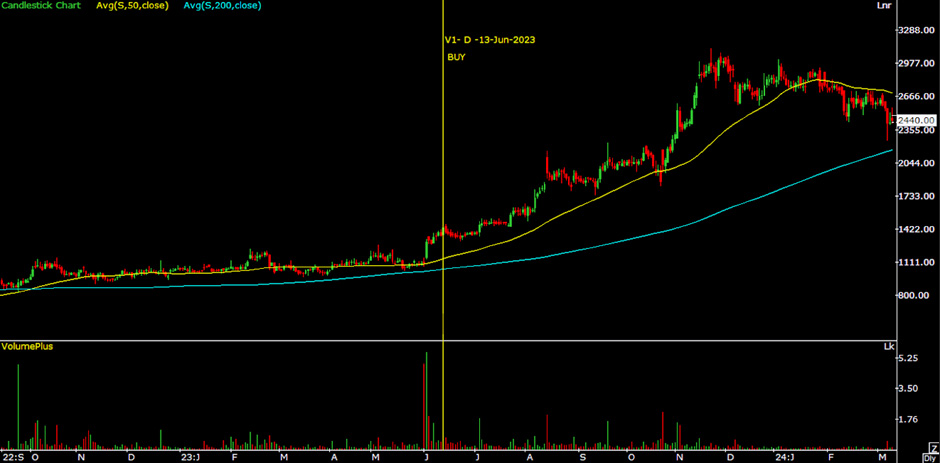
KDDL Ltd. was included in our watchlist on June 13th, 2023 because the stock was trading 26% higher than the 50-day moving average and 37% higher than the 200-day moving average on a daily chart. Upon conducting a thorough analysis of the company's fundamentals, we confidently recommended a buy rating for this stock. Our customers experienced a 71% increase in returns from their investments in KDDL.
Moving Averages in Action: Case Study 2
In another scenario, let's explore how moving averages can be used to manage risk and optimize trade entries and exits. By setting dynamic stop-loss orders based on moving average levels and trailing the stop-loss as the trend progresses, investors can protect their capital while maximizing profits in trending markets.
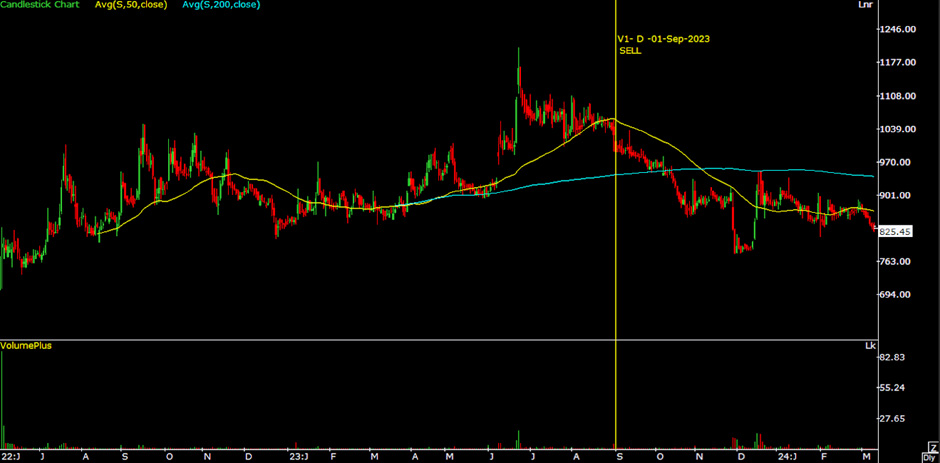
On September 1, 2023, we advised selling the stock of Aether Industries Ltd. for 1005, as the stock was trading 6% below its 50DMA and 5% above its 200DMA on a daily chart. Since then, the stock has been consistently declining. Presently, the stock is trading below its significant moving averages at 827.
Common Pitfalls and Risk Management
Overreliance on Moving Averages
While moving averages can be powerful tools in stock trading, overreliance on them can lead to suboptimal decision-making and missed opportunities. It's essential for investors to complement moving averages with other technical indicators, fundamental analysis, and market sentiment assessments to gain a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
Risk Management Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with trading, it's crucial for investors to implement robust risk management strategies. This includes setting stop-loss orders based on moving average levels, diversifying trading portfolios, and adhering to disciplined trading plans. By managing risk effectively, investors can safeguard their capital and improve long-term profitability.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
In conclusion, mastering moving averages is a fundamental aspect of successful stock trading. By understanding their calculation methods, interpretation techniques, and practical applications, investors can gain valuable insights into market trends and make informed decisions. As technology evolves and trading methodologies continue to evolve, the role of moving averages in stock trading is likely to remain prominent, serving as indispensable tools for investors of all levels.

















 Continue with Google
Continue with Google